Breast reduction in Paris: Treatment, prices and before and after effects
Breast reduction: what are the benefits?
Breast reduction, or reduction mammoplasty, is much more than a cosmetic procedure; it's a restorative surgical procedure that profoundly transforms patients' daily lives. By reducing both breast volume and ptosis (sagging), the result is lighter, higher and better-proportioned breasts. Beyond the visual aspect, the physical and psychological benefits are numerous:
- Reduced chronic pain (back, shoulders, neck) thanks to lighter breast weight.
- Improved posture and overall comfort, with a sensation of body liberation.
- A new-found ease of physical activity, without discomfort.
- Reduces skin irritation under the breasts, often caused by rubbing or dampness.
- A complete aesthetic result, with breasts that are redesigned, lifted and better proportioned to the figure.
- Enhanced self-confidence, thanks to a more harmonious silhouette and lighter, lifted breasts.
Breast reduction provides a concrete response to the physical pain and complexes associated with large breasts, for lasting well-being.
Breast reduction definition: what does it involve?
Breast reduction, also known as breast reduction surgery, is a surgical procedure designed to reduce the volume of the breasts while improving their shape and position. It is primarily intended for women suffering from overly large breasts, often a source of back pain, discomfort in daily life or aesthetic complexes.
The procedure involves removing excess mammary gland, fat and sometimes skin, usually from the lower part of the breast. The remaining tissue is then reshaped to create firmer, higher breasts that are more in harmony with the figure. The nipple and areola are repositioned to a more anatomically natural area at the top of the new breast shape.
Several surgical techniques are available, depending on the degree of reduction required and the elasticity of the skin. In the majority of cases, scars are in the shape of an inverted T (or "sea anchor"), combining a vertical incision and a horizontal incision in the submammary fold. In some younger patients or those with moderate hypertrophy, a vertical scar alone may suffice.
In very rare cases, we can even even offer breast reduction by liposuction, enabling us to achieve a result with scars of less than 1 cm.
This operation brings real physical comfort and lasting aesthetic improvement, while preserving breast sensitivity and the possibility of breastfeeding in most cases.
Breast reduction: procedure
If you have a family history of breast cancer, you may be asked to have a mammogram and an ultrasound.
Breast reduction is performed under general anesthesia. This requires a pre-anesthetic consultation at least 48 hours before the procedure.
In the majority of cases, the operation is performed as a conventional hospital procedure (entry at 1pm, discharge at 11am the following day), but it can also be performed as an outpatient procedure (entry at 8am, discharge at 6pm).
The operation is not very painful, but the post-operative care requires you to stop working for 7 to 21 days, depending on how arduous your job is.
Our specific breast reduction surgery technique
Unlike the majority of our French colleagues who use a superior pedicle technique, we use a specific operative technique (superior-internal pedicle technique) described by a Canadian surgeon (Elisabeth Hall-Findlay).
This technique has the great advantage of not separating the areola and the nipple from the underlying gland. This allows :
- Avoid almost all risk of areola and nipple necrosis (5% of cases with the superior pedicle technique)
- greatly improve the postoperative sensitivity of the areola and nipple and preserve this erogenous zone
the possibility of breastfeeding after breast reduction (impossible with the superior pedicle technique).
This technique also allows to limit the important tissue detachments and to allow an ambulatory breast reduction surgery without placing a Redon drain.
Questions / Answers about breast reduction
What are the possible complications of a breast reduction?
The main complication is altered sensitivity of the areola and nipple. This may persist in the long term, but the risk is greatly reduced when we use the superior-internal pedicle surgical technique.
A hematoma or blood clot may occur on the evening of the operation, but this is extremely rare.
In the case of very large breasts, suffering of the areola may occur, with 5% of cases requiring areola grafting during or the day after the operation.
Breast reduction scars: how long after surgery?
Scars after breast reduction are initially thick and inflammatory for the first 3 months, then diminish sharply up to 18 months after surgery.
Painful breast reduction: how long does the pain last?
Breast reduction is generally well tolerated in terms of pain. Post-operative sensations are often described as moderate tugging or discomfort, rather than intense pain. This procedure does not affect the muscles, which considerably limits discomfort. Appropriate painkillers are prescribed to relieve the initial sensations, and most patients regain a good level of autonomy within a few days. Slight burns around the scars may persist temporarily, but gradually subside.
Breast reduction: What is the post-operative care after surgery?
Post-operative care is relatively straightforward.
The day after the operation, the drains are removed by the nurse and care is provided after a shower.
This consists of disinfecting the scar, followed by placing bandages or compresses in the sports bra.
This care is repeated every day at home for 15 days, possibly with the help of a nurse for the first few days.
The support bra must be worn at all times for up to 3 weeks after the operation.
How long should I wear a bra after a breast reduction?
After a breast reduction, a support bra should be worn at all times for up to 3 weeks after the operation.
Breast reduction cup: What will my cup look like after the operation?
The majority of patients requiring a breast reduction have a cup size larger than an E.
In order to maintain a harmonious breast shape, it is necessary to keep a breast volume equivalent to a C cup.
Some women prefer a B cup, but should be warned that the breasts may be a little flat and less aesthetically pleasing.
Breast reduction and breastfeeding: Can I breastfeed after a breast reduction?
Thanks to the technique we use (superior-internal pedicle technique), breastfeeding is possible after breast reduction, which is generally not the case with the classic superior pedicle technique. The classical technique separates the areola from the underlying gland, and the milk ducts are cut off, which is why we have decided to stop performing this technique.
Breast reduction Price: how much does a breast reduction cost?
Health insurance covers breast reductions where the glandular resection is greater than 300g per operated breast.
In practice, this corresponds to a large D cup and above.
In these cases, we charge additional fees ranging from 3,500 to 4,000 euros, which may be covered by your supplementary health insurance.
If the planned glandular resection is less than 300g, the price of a breast reduction corresponds to that of a simple aesthetic ptosis cure (from 7,500 to 9,000 euros).
Breast reduction reimbursed: is reimbursement possible?
A breast reduction may be reimbursed by the Assurance Maladie under certain conditions. To be reimbursed for a breast reduction, the operation must remove a minimum of 300 grams per breast, which is essential if the operation is to be considered reconstructive rather than cosmetic. This assessment is made during the consultation with your plastic surgeon.
Please note that additional fees are the patient's responsibility and may be reimbursed by your complementary health insurance.
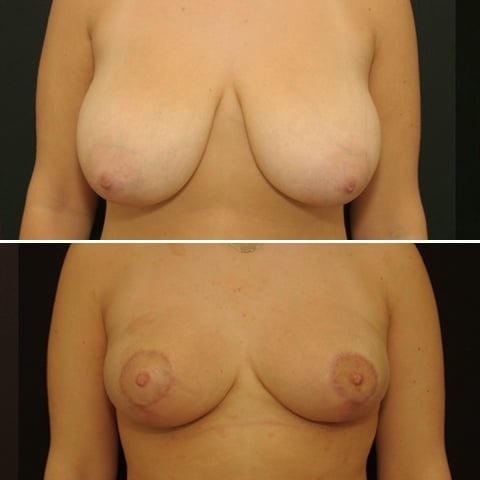
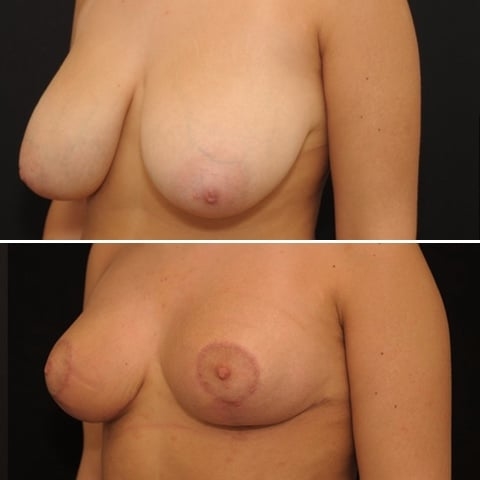
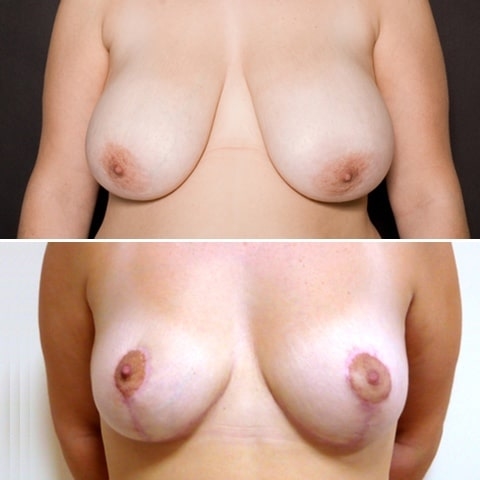
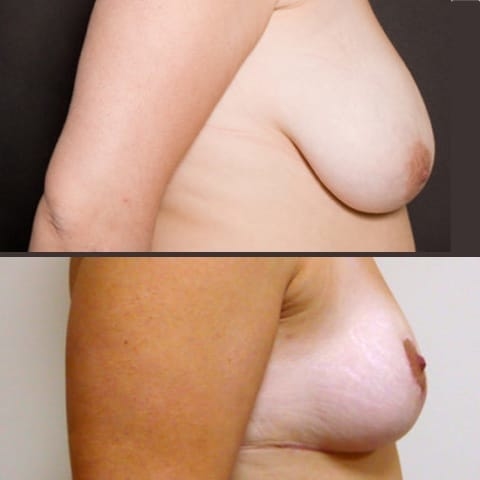
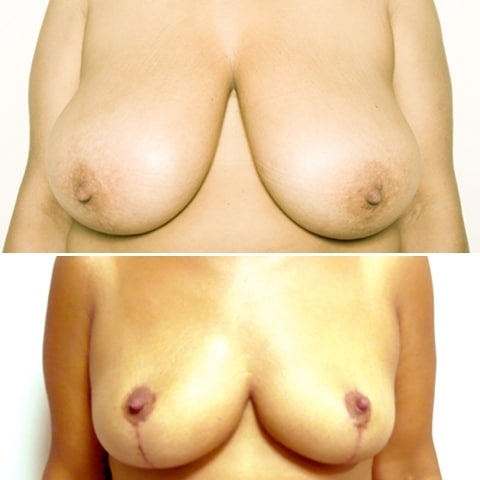
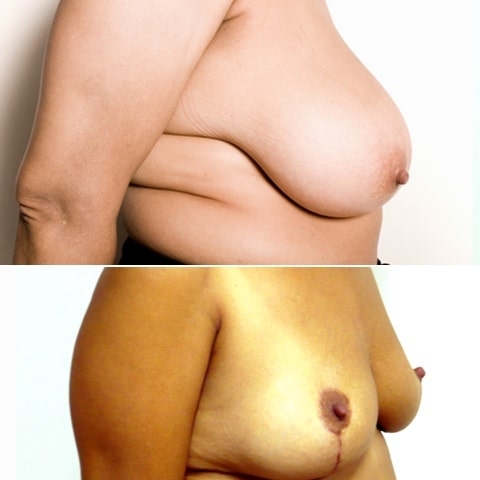
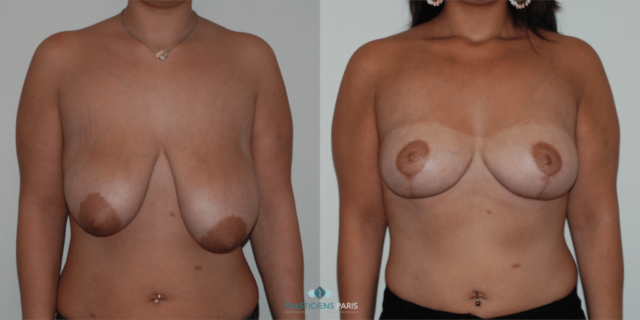
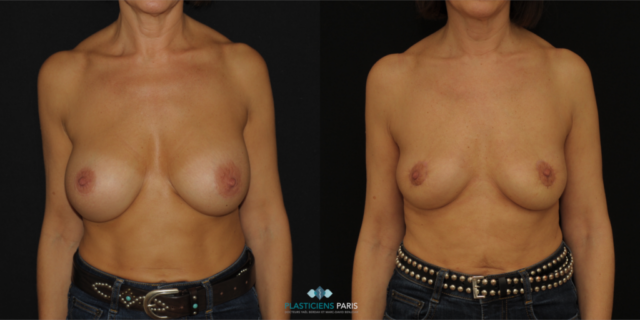
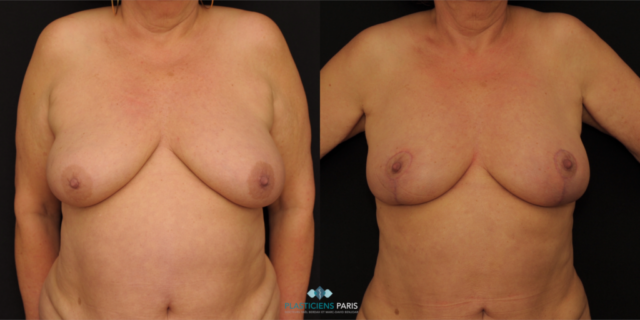
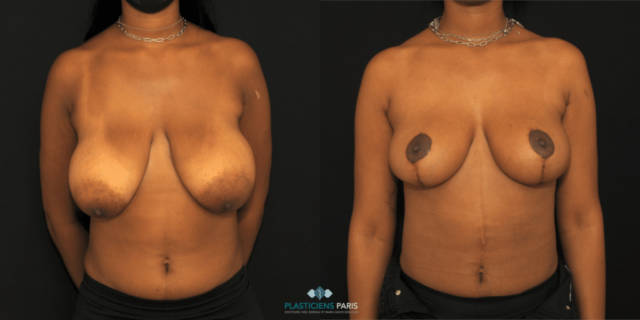
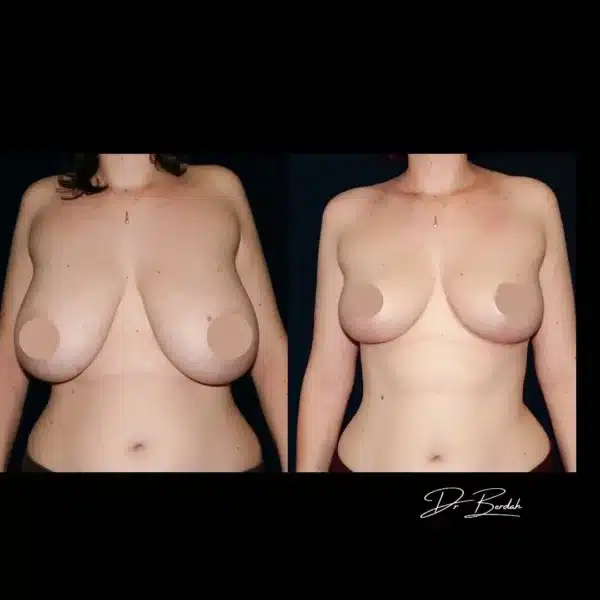
Before and after breast reduction: breast reduction photos
Discover before-and-after photos of breast reduction results, performed by Dr. Benjoar and Dr. Berdah, breast surgeons in Paris for over 15 years.
F cup breast reduction before after
See the results of an f-cup before-and-after breast reduction with inverted-T scars after removal of 700 grams per breast. Photo at 6 months.
Have a question? Please contact us!
Cosmetic surgery in Paris
Docteur Yaël Berdah and Docteur Marc-David Benjoar
Plastic surgeons in Paris France